Introduction
In the realm of financial markets, candlestick patterns shine as invaluable tools for traders seeking to navigate the complexities of price movements and make informed decisions. These patterns offer insights into market sentiment, helping traders predict potential reversals and trend continuations. This article dives deep into the world of candlestick patterns, unraveling their significance, types, and strategies to enhance your trading prowess.
Candlestick patterns hold a pivotal role in technical analysis, offering a visual representation of price data. They provide traders with an immediate glimpse into the battle between buyers and sellers, shedding light on market psychology. By utilizing the term “candlestick patterns” throughout this article, we aim to enhance your understanding and mastery of this trading tool.
Understanding Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns depict the price movements within a designated timeframe through visual representations. Each candlestick consists of four key elements: the opening price, closing price, highest price (high), and lowest price (low). The body of the candlestick represents the range between the opening and closing prices, while the wicks (upper and lower shadows) extend beyond the body, indicating the high and low points reached during the timeframe.
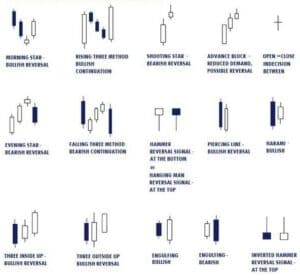
The Significance of Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns offer traders a unique perspective on market sentiment and potential price reversals. These patterns can signal the weakening of a trend or its continuation. For instance, a bullish candlestick pattern like the “Hammer” suggests a potential bullish reversal, while a bearish pattern like the “Shooting Star” indicates a possible bearish reversal.
Common Candlestick Patterns
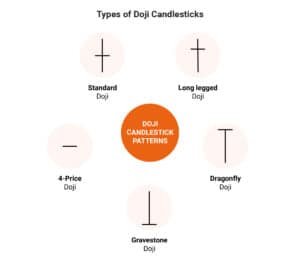
1. Doji Pattern:
A Doji pattern forms when the opening and closing prices are virtually the same. It signifies market indecision and can signal a potential trend reversal.
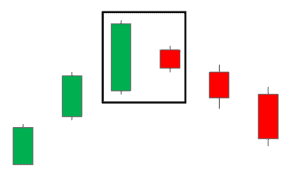
2. Bullish Engulfing Pattern:
This pattern occurs when a smaller bearish candle is followed by a larger bullish candle that engulfs it. It suggests a bullish reversal may be on the horizon.

3. Bearish Harami Pattern:
A bearish candle followed by a smaller bullish candle characterizes the Bearish Harami. It could suggest the continuation of a bearish trend.
Candlestick Pattern Strategies
Mastering candlestick patterns requires a strategic approach. Below are several important strategies to take into account:
1. Identify Confluence Zones
Combine patterns with other technical indicators, such as moving averages or trendlines, to identify confluence zones. These areas enhance the reliability of your trading decisions.
2. Practice Patience
Don’t jump into trades solely based on a single candlestick pattern. Wait for confirmation through subsequent price action before making your move.
3. Utilize Multiple Timeframes
Analyze patterns across different timeframes to gain a comprehensive view of market dynamics. Patterns that coincide across different timeframes hold greater significance.
FAQs:
Q: Can candlestick patterns be used in all financial markets?
A: Yes, they are applicable to various markets, including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
Q: How can beginners effectively learn to interpret candlestick patterns?
A: Beginners can start by studying the basic patterns and gradually expanding their knowledge. There are many online resources and educational materials available for learning.
Q: Are candlestick patterns 100% accurate in predicting price movements?
A: While they provide valuable insights, they are not infallible. External factors and unexpected events can influence market movements.
Q: Can I solely rely on candlestick patterns for my trading decisions?
A: While these patterns offer valuable information, successful trading involves a holistic approach that considers multiple indicators and factors.
Q: What is the significance of the color of the candlestick body?
A: In many charting platforms, a bullish candlestick is often depicted in green or white, while a bearish candlestick is shown in red or black.
Q: How can I avoid common pitfalls when using candlestick patterns?
A: Avoid overtrading, and always practice risk management. Additionally, continually expand your knowledge and stay updated on market trends.
Q: Are there any specific patterns that are more suitable for day trading?
A: Yes, certain patterns like “Morning Star” and “Evening Star” are often favored by day traders due to their potential for quick trend reversals.
Q: Can chart patterns help in identifying support and resistance levels?
A: Absolutely, these patterns can aid in identifying key support and resistance levels, providing valuable insights for entry and exit points.
Q: Do these patterns work well in volatile markets?
A: Yes, they can be effective in volatile markets, as they reflect rapid shifts in sentiment and can help traders adapt to changing conditions.
Q: How frequently should I review patterns on my charts?
A: It’s recommended to review your charts regularly, ideally on a daily basis, to stay updated on evolving patterns and market dynamics.
Conclusion
Candlestick patterns are more than just visual elements on a trading chart; they are windows into market psychology and potential price movements. By understanding and effectively utilizing these patterns, traders can enhance their decision-making process and increase the likelihood of profitable trades. Remember, success in trading requires continuous learning and adaptation to changing market conditions.
